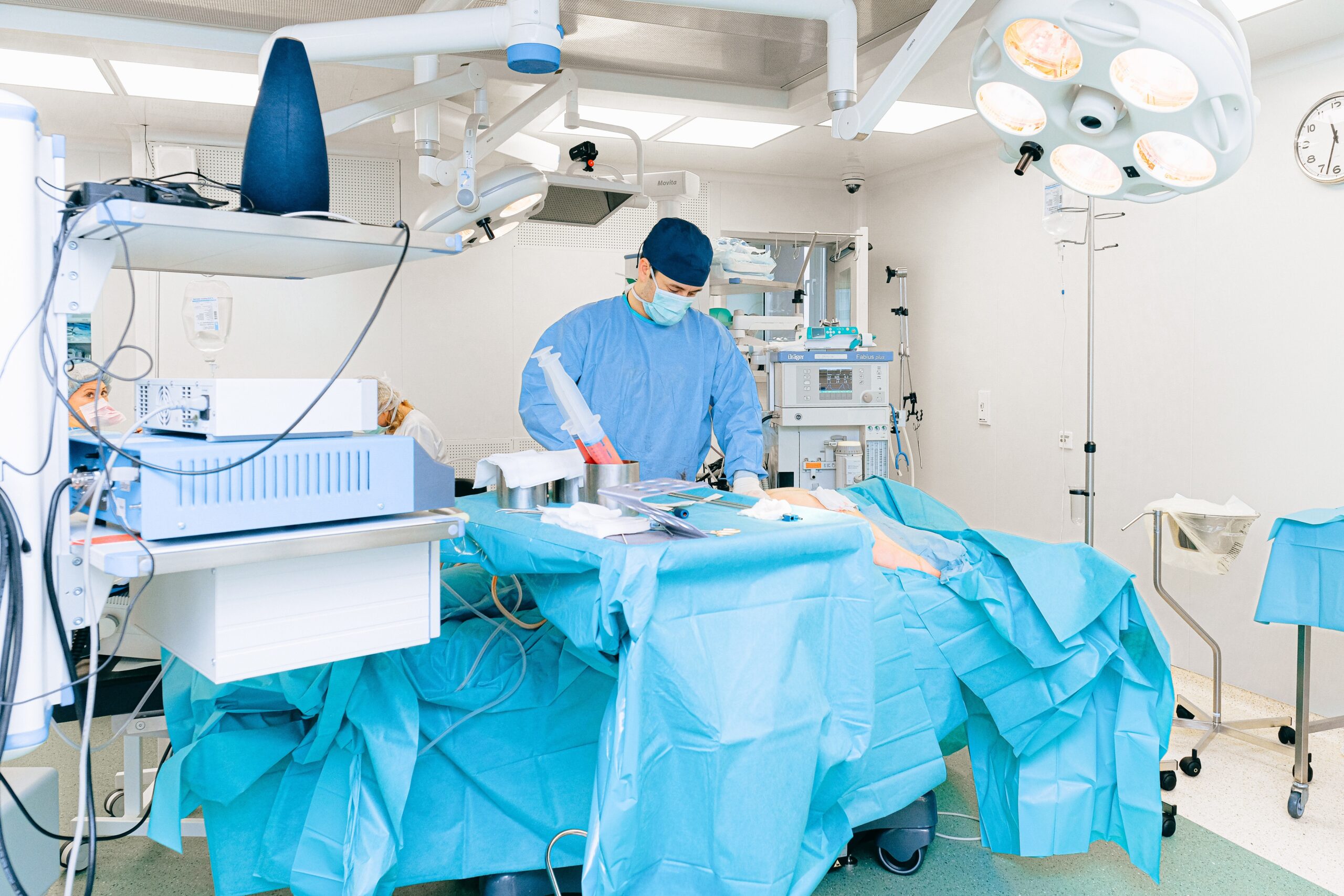
Overview
To have a better look at your reproductive organs and the organs in your abdomen, you may need to have a laparoscopy performed. This treatment may assist in the diagnosis of a variety of medical disorders and the collection of biopsies – samples of tissue that are analyzed. In addition, a laparoscopy is a technique that is typically safe and has minimal problems.
Every year, about 15 million laparoscopic operations are done worldwide, with the United States accounting for nearly a third of the total, or around 4,800,000 procedures.
Everything You Need To Know About General Laparoscopic Surgery
- What Is It
- Common conditions
- Procedure
- Conclusion
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
A laparoscopy is a technique that is performed to examine the organs in the abdomen (abdomen). It may also be used to examine a woman’s pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy is performed using a narrow, illuminated tube that is equipped with a video camera. A laparoscope is a name given to the tube. It is inserted into a small cut or incision in your stomach. The pictures captured by the video camera may be viewed on a computer screen.
One of the advantages of laparoscopy is that it is a less intrusive procedure. That is to say; it makes a very little incision in the stomach. As a result, laparoscopic surgery is often less time-consuming and results in a quicker recovery period than open surgery.
A laparoscopy procedure may be performed to obtain a tiny tissue sample for laboratory testing (a biopsy). Moreover, it may be utilized to remove organs such as the appendix (appendectomy) or the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
Common Conditions treated by it
To detect and diagnose the cause of pelvic or abdominal discomfort, laparoscopy is often performed. In addition, it is often used when noninvasive approaches are ineffective in diagnosing a condition.
It is also possible to identify abdominal disorders using imaging methods such as those described below:
- Ultrasound, which is a medical procedure that creates pictures of the body by using high-frequency sound waves.
- In contrast to conventional radiography, CT scanning uses specific X-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the body.
- An MRI scan is a kind of imaging procedure that produces pictures of the body by using magnets and radio waves.
- When these tests fail to offer enough information or insight to diagnose, laparoscopy is done to help make the diagnosis.
- Additionally, the surgery may be performed to get a biopsy, a sample of tissue, from a specific organ in the abdomen.
Your doctor may propose laparoscopic surgery to evaluate the organs listed below:
- Appendix
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Small intestine and large intestine (colon)
- Pelvic or reproductive organs
- Stomach
Your doctor may discover the following conditions by using a laparoscope to examine these areas:
- A lump or tumor in the abdomen
- The presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity
- Liver disease
- The effectiveness of certain treatments
- The extent to which a specific malignancy has progressed
In addition, your doctor may be able to execute an intervention to address your illness as soon as possible when it is discovered.
Procedure
A laparoscopic procedure is performed when you are lying down in a moderately slanted posture, with the head lower than the feet. During surgery, you will be provided anesthesia to calm your muscles and keep you from feeling pain.
Following that, a tiny incision is made close to the navel. Through this incision, the laparoscope is placed into the patient. Your abdomen has been expanded to make your organs more visible. The laparoscope may be outfitted with surgical equipment for obtaining tissue samples or eliminating scar tissue during the procedure.
It is also possible that laparoscopic physicians may make a second incision near the pubic hairline. This incision offers an extra entry for the required tools for minor surgical operations to be completed.
After surgery, you’ll typically be in the recovery room for approximately an hour after the procedure. Then, a little time later, you’ll be transferred to an outpatient surgery facility for further observation.
After completing your home rehabilitation instructions, you will be released. In most circumstances, you will be able to leave the hospital within four hours after having a laparoscopy. It is quite unusual for a patient to be required to remain in the hospital overnight after this treatment.
Following your laparoscopy, you will be required to return to your healthcare provider’s office for follow-up sessions within two to eight weeks following the procedure. Please check your follow-up appointment schedule with your healthcare practitioner before leaving the hospital.
Before having surgery, one thing to keep in mind is that you will not be allowed to drive for at least 24 hours following the procedure. So prepare for the possibility of having someone come pick you up and remain with you for the first 24 hours after your arrival.
Conclusion
With laparoscopy, doctors may identify and treat a wide range of gynecologic problems on an outpatient basis. Compared to abdominal surgery performed via bigger incisions, the recovery period for patients is very short and much shorter. Patients should speak with their doctors about their concerns regarding laparoscopic procedures and the dangers associated with them before having the surgery.

